How to maintain good vision amidst the myopia epidemic

Vision in the Digital Age
How to maintain good vision amidst the myopia epidemic

If you lost one of your senses, which one would you least want to lose? For many people, it’s vision.
Yet that’s exactly what’s happening today.
A New Epidemic
Myopia, the medical term for nearsightedness, is an epidemic. 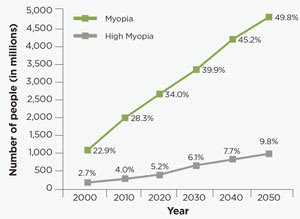
If you have myopia, you will need glasses to see clearly. Needing them every day and paying for them is maybe a minor to moderate inconvenience in your life.
If you have high myopia, you need glasses stronger than -5.00. Wearing glasses is now definitely an inconvenience, because you are very dependent on them to see. They are expensive, and if you want glasses, they are going to be thick (thicc) and goofy. You are also legally blind without glasses or contacts.
Even worse, if you have high myopia, you are at a much higher risk of retinal detachments, cataracts, and losing your vision completely.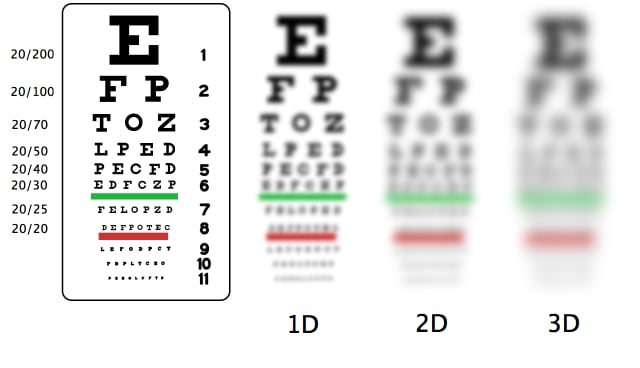
How did we get to this point? Shouldn’t visual health be getting better in 2024, not worse?
Our Visual System
Let’s talk a little bit about our visual system.
Focus
When something is in focus, it’s clear. But why exactly is it clear?
It’s clear because your eye has taken the light from that object and projected it precisely onto your retina. Not behind it, not in front of it.
More specifically:
light diverges from millions of small points on the object and some of that light hits your eyes
your eye uses refraction to bend that light, so that they converge to small points again
your eye uses the right amount of refractive power so that each point converges directly at the retina, not in front of it or behind it
the photosensitive cells (rods and cones) of your retina receive a sharp image
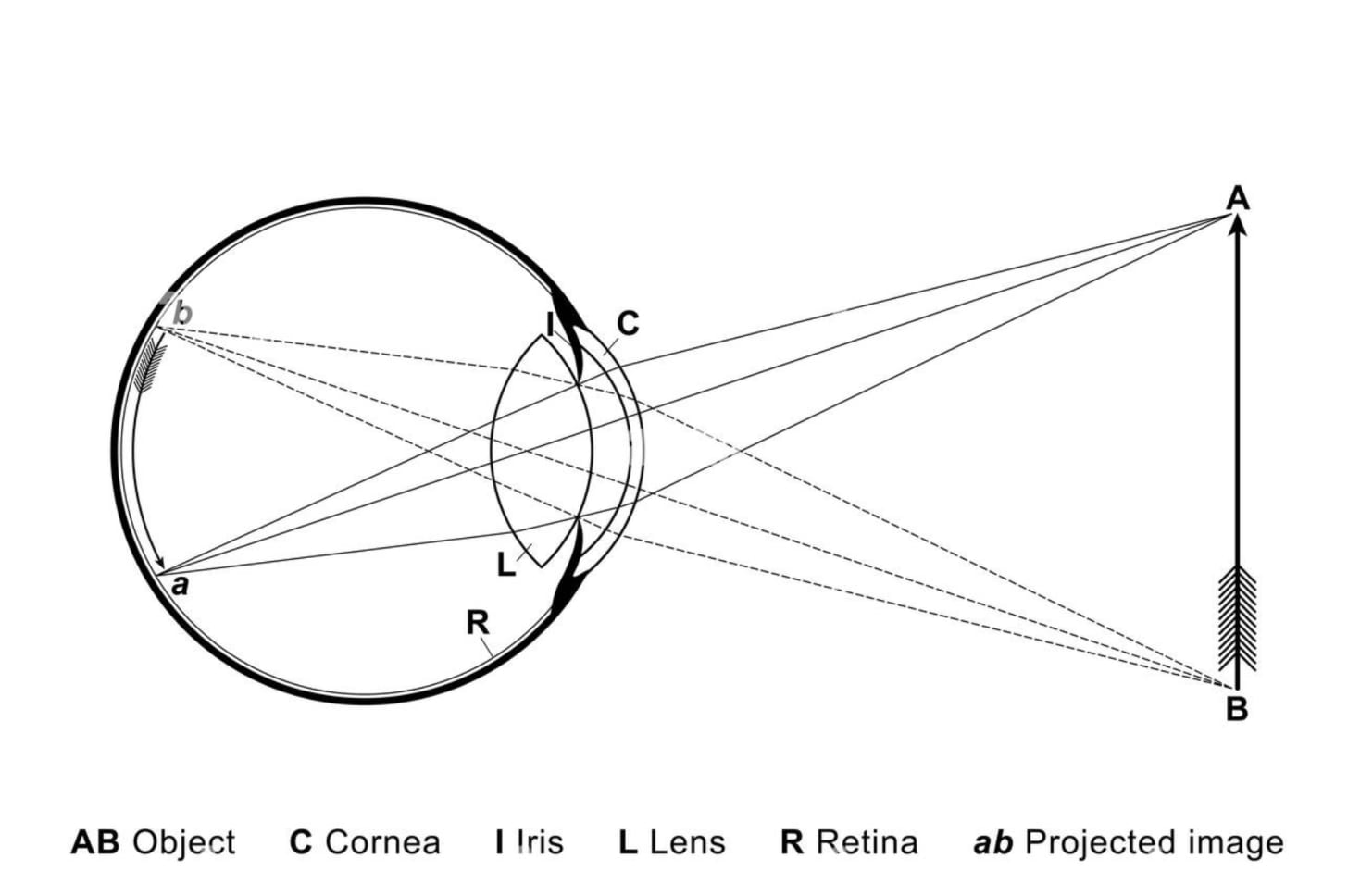
It’s impossible for your eye to focus on multiple objects at once. For example, put your finger up to your face and try focusing on it and the surroundings behind you at the same time.
Accommodation
Although you can’t focus on multiple objects at once, you can still choose where to focus - near or far.
Near points of light diverge into your eyes at a sharp angle and your eyes need more refractive power to bend them onto the retina.
Far points of light diverge at a gentler angle and your eyes need less refractive power to focus them onto the retina.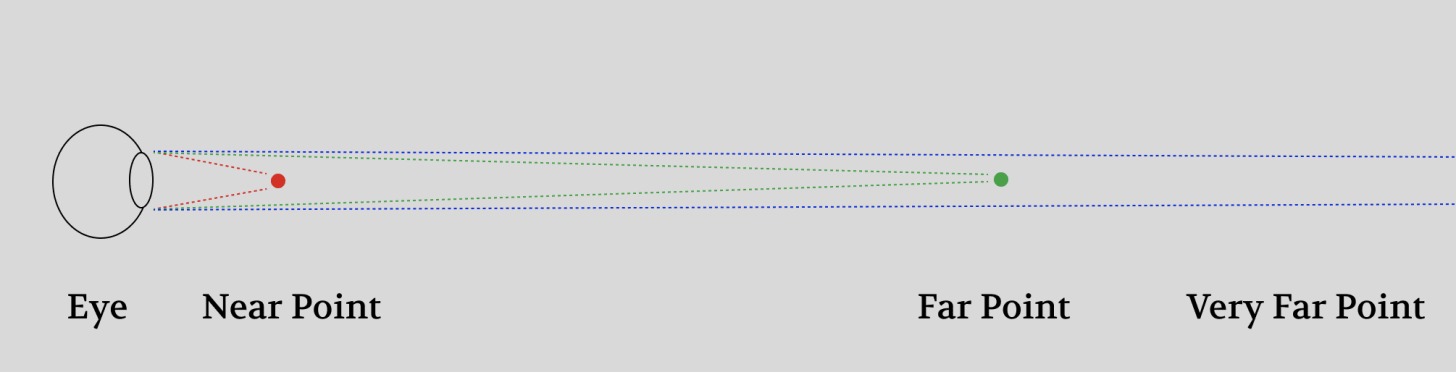
In order to vary the refractive power to focus near or far, muscles make your eye lens physically thicker or thinner. A thicker lens has more refractive power than a thinner one.
The process of adjusting focus is called accommodation.
Normal Range of Clear Vision
People with good vision can use accommodation to see clearly over a wide range of distances. 
When fully relaxed, their eyes can technically see an object at an infinite distance away (zero angle of light divergence).
Nothing is actually infinitely far away, but they can see extremely far away objects clearly, such as stars in the night sky.
Myopic Range of Clear Vision
People with myopia have a different range of clear vision.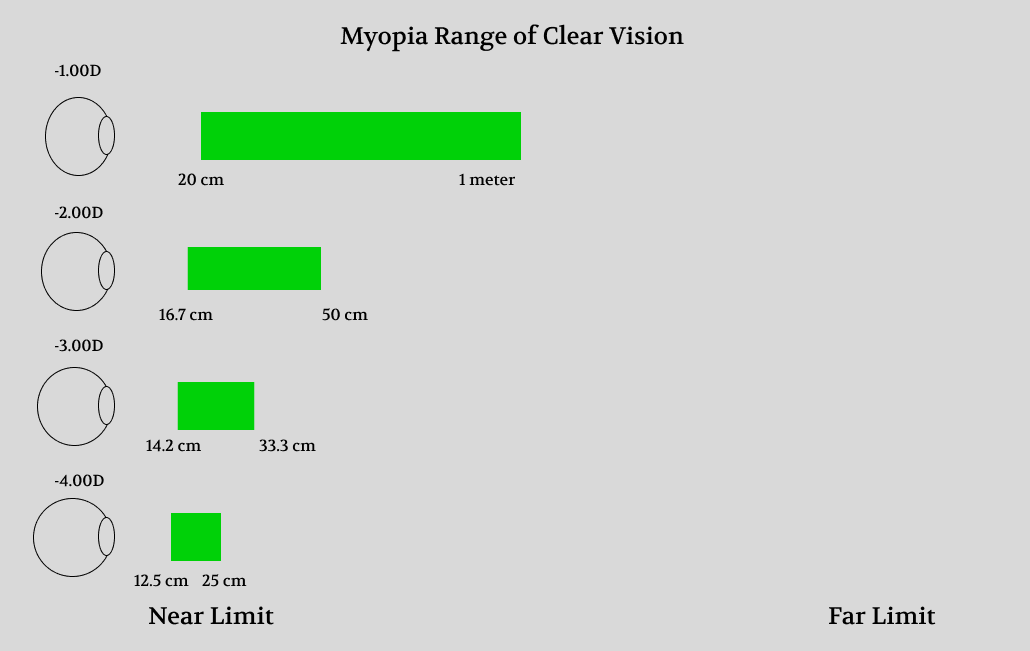
A common reason for this is that the eyeball grows too long, and the retina is therefore further behind the lens than normal.
Even when myopic eyes are fully relaxed, they have too much refractive power, and far points of light converge before the retina.
Myopia Causes
What makes people get myopia?
Like many things, there are environmental and genetic reasons.
A massive, massive reason is the environment we place ourselves in, specifically:
time spent outdoors
time spent looking at things in the distance (10+ yards away)
The more of the above you do, the lower your chance of getting myopia.
Genetics is also a factor. If your parents have myopia, it’s more likely that you will have it too.
But genetics cannot explain the insane rate of change of myopia over the past 50 years. A rapid change in our environment can.
The Elephant in the Room
Has there been a rapid change in our environment and lifestyles over the past 50 years?
I think you already know the answer. Screens, computers, smartphones.
Screens are simply not good for our eyes. Here are a few reasons:
we mostly use them indoors
they are mostly in our near vision
they are flat
Because screens are mostly used indoors in near vision, they constitute the two biggest environmental risk factors for myopia. Indoor time and near work are both strongly associated with myopia, especially in childhood.
Because screens are flat, they confuse and strain our visual system, which evolved to perceive depth (almost everything in the natural world has physical depth). In addition to myopia, this strain leads to myriad other symptoms, collectively known as computer vision syndrome.
Screens have moved closer and closer to our eyes over time, adding more and more strain. Think old movie theaters, then televisions, then personal computers, then laptops, then smartphones.
We also spend dramatically more time on screens compared to decades ago. 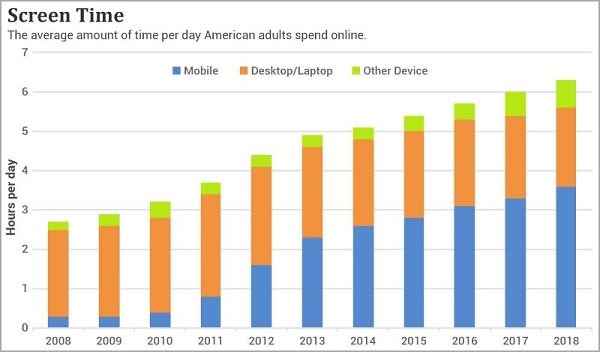
The fact that myopia is exploding is no coincidence.
Remember how your eye muscles contract to look at near objects and relax to look at distant objects?
When we look at screens, our eyes are contracted. Too much continuous screen time can lead to those muscles getting locked up - it’s called accommodative spasm and directly causes blurry distance vision.
Think of it like clenching your fist whenever you look at a screen, tightly for computers and even tighter for smartphones. Clench your fist for 8 hours a day, every day. When you need to look at something far away, i.e. for driving, fully open your hand.
It’s going to be a little harder to open your fist if it’s been tightly clenched for most of the day. And that’s essentially what’s happening in our eyes.
Do you spend a lot of time looking at screens?
Myopia Prevention
Even if you do, you still have the opportunity to have great visual health. There are preventative steps that you can take that will:
significantly lower your chance of getting glasses for myopia
lower your chance of stronger glasses if you already have glasses
The preventative steps are simple:
spend time outdoors
spend time looking at things far away
The ideal scenario is getting 2 hours of outdoor time a day, and using the 20-20-20 rule if you have a lot of screen time.
Again, these practices are preventative and can prevent myopia or prevent existing myopia from getting worse.
If you’re interested, here is a very detailed guide of more preventative things you can do for your eyes.
Myopia Correction
There are also corrective steps that you can take if you have myopia. We all know about these - basically it means get glasses, contacts, or surgery.
Obviously, the main benefit of corrective options is that you can see clearly. You pretty much need correction if you have myopia, unless your myopia is very mild.
You can also get surgery - I know a bunch of people that got LASIK and are super happy with the results.
The shortcoming of corrective options is they don’t fix the underlying problem with your eyes.
Glasses and contacts are a prosthetic - just like crutches are. Your eye is still nearsighted as soon as you take them off. You are still at risk of vision loss if you have high myopia.
Getting LASIK is kind of like burning a contact lens onto your eye. Your eye is still nearsighted, but you have a “contact lens” on your eye that you can never take off. After LASIK, you are still at risk of vision loss if you have high myopia.
Overall, corrective options for myopia are basically required if you want to see clearly in your daily life.
Many people are happy with corrective options.
However, they do not fix the underlying problem with your eye. This is especially notable if you have high myopia, around -5.00D or worse, because the underlying problem could still lead to serious complications.
Myopia Reversal
Is there a way to fix the underlying problem with your eye?
According to some people, there is a way to reverse myopia. Here is a guide that claims how to do so, here is a second guide, and here is a third.
These methods are not generally validated by the scientific community.
In fact, many people say that myopia reversal is a lie. Others claim to have successfully reversed their myopia to varying degrees.
In my opinion, it’s too early, too ambiguous, and the jury is out on whether myopia can actually be reversed.
Wrapping Up
Myopia, or nearsightedness, is a massive problem. 50% of the world is going to need glasses because of it, and 10% of the world is going to need glasses so strong that they are a) legally blind without them and b) are at risk of losing their vision completely.
These percentages have skyrocketed since just 2000, increasing by 200% and 400%, respectively by 2050.
You may be someone with myopia. I am too.
The elephant in the room is digital screens, which have recently become ubiquitous in our lives, and are damaging to our eyes.
The more time we spend on screens, the more time we spend indoors and in near vision, which contributes to myopia and computer vision syndrome.
Computers are not going away, but there are still preventative and corrective actions that you can take to protect your vision. There are (not clinically proven) claims that you can even reverse myopia.
Stay Tuned
Another great thing you can do to protect your vision is stay tuned. I’ve been working on new ways to protect your vision in a digital world :)
Thanks for reading,
Sohil
Thanks for reading Sohil’s Substack! Subscribe for free to receive new posts and support my work.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26875007/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4675264/
https://www.nature.com/articles/eye2013254
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0